Glutamine: Benefits, Side Effects , And More
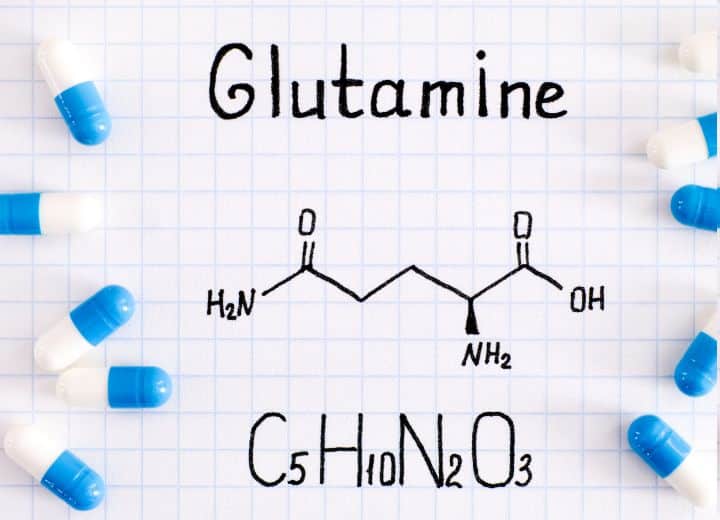
Glutamine is a crucial amino acid that plays multiple roles in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is involved in protein synthesis, immune system function, and digestive health.
Found abundantly in various foods like meat, poultry, dairy products, and certain plant-based sources, glutamine is also available in supplement form for those needing additional support.
Its benefits range from promoting muscle growth and recovery to aiding in immune system support and even assisting in medical treatments. Incorporating glutamine into your diet or supplementation regimen can contribute to optimal health and vitality.
What Are Different Benefits of Glutamine?
Glutamine, an essential amino acid, offers numerous benefits for overall health and well-being:
Muscle Growth and Repair:
It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, facilitating muscle growth and repair. It is particularly beneficial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking to enhance muscle mass and recover faster from intense workouts.
Immune System Support:
Glutamine is vital for the proper functioning of the immune system. It helps boost the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections and illnesses. Regular glutamine intake may help strengthen the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Digestive Health:
Glutamine is a primary fuel source for the cells lining the digestive tract. It helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream. This can aid in improving digestive health and reducing symptoms of conditions like leaky gut syndrome and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Enhanced Athletic Performance:
Glutamine supplementation has been shown to improve exercise performance and reduce fatigue during prolonged physical activity. It may also help decrease muscle soreness and enhance endurance, allowing individuals to train harder and longer.
Wound Healing:
It plays a critical role in wound healing and tissue repair. It promotes collagen synthesis and accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues, making it valuable for individuals recovering from surgery, injuries, or burns.
Stress Reduction:
During times of physical or psychological stress, the body’s demand for glutamine increases significantly. Supplementing with it may help alleviate stress-related symptoms and promote overall well-being by supporting the body’s stress response mechanisms.
Supports Gut Health:
Glutamine is essential for maintaining the health of the intestinal lining and supporting optimal digestive function. It can help alleviate symptoms of conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and leaky gut syndrome by promoting gut barrier integrity and reducing inflammation.
Enhanced Brain Function:
Glutamine is a precursor to neurotransmitters like glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which play key roles in brain function and mental health. Adequate levels may support cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
Incorporating glutamine-rich foods into your diet, such as meat, fish, dairy products, tofu, beans, and legumes, can help ensure an adequate intake of this essential amino acid. Additionally, glutamine supplements are available for those who may need additional support, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
What Are The Different Side Effects of Glutamine?
, while generally considered safe for most people when consumed in appropriate amounts, may cause side effects in some individuals, particularly when taken in high doses or for extended periods. It’s essential to be aware of these potential side effects before incorporating supplements into your routine:
Gastrointestinal Distress:
One of the most common side effects of glutamine supplementation is gastrointestinal discomfort, including symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. These symptoms are more likely to occur when taking high doses of it or if you have a sensitive stomach.
Allergic Reactions:
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to glutamine supplements, though this is rare. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include itching, rash, hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, or tightness in the chest. If you experience any of these symptoms after taking this, discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention.
Exacerbation of Manic Symptoms:
Glutamine supplementation has been reported to exacerbate manic symptoms in individuals with bipolar disorder or other mood disorders. If you have a history of mood disorders, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking its supplements to avoid potential adverse effects.
Interference with Certain Medications:
Glutamine supplements may interact with certain medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, it may interact with chemotherapy drugs, leading to increased toxicity or reduced efficacy. If you are taking any medications, particularly those for cancer treatment or immune system disorders, consult with your healthcare provider before using its supplements.
Risk of Hyperammonemia:
In rare cases, excessive glutamine supplementation may lead to elevated levels of ammonia in the blood, a condition known as hyperammonemia. This can cause symptoms such as confusion, lethargy, weakness, seizures, and coma. Individuals with liver disease or urea cycle disorders may be at a higher risk of developing hyperammonemia when taking its supplements.
Potential for Increased Blood Sugar Levels:
Glutamine is converted into glucose in the body, which may lead to increased blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance. Monitoring blood sugar levels closely and adjusting medication doses as necessary may be required for individuals with diabetes who are taking it’s supplements.
Kidney and Liver Function:
Excessive intake of glutamine supplements may put additional strain on the kidneys and liver, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions. It’s essential to monitor kidney and liver function regularly when taking supplements, especially at higher doses.
It’s crucial to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health needs and help you weigh the potential benefits against the risks of supplementation.
What Are Different Interactions of Glutamine?
Glutamine supplements may interact with medications used to treat seizures, potentially affecting their efficacy or side effects. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before combining with seizure medications to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Also Read: 8 Benefits Of Apple Cider Vinegar
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is it safe for everyone?
It is generally safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, certain individuals, such as those with specific medical conditions or allergies, may need to avoid it.
Can glutamine supplements cause side effects?
While rare, its supplements may cause side effects such as gastrointestinal distress or allergic reactions in some people.
Can glutamine interact with medications?
Yes, supplements may interact with certain medications, including anticonvulsants and chemotherapy drugs. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting glutamine supplementation if you’re taking any prescription medications.
How should I take glutamine supplements?
It’s advisable to start with a low dose of it and gradually increase it as tolerated to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Additionally, it’s essential to follow the dosage recommendations provided by your healthcare professional or the product label.
Should pregnant or breastfeeding women take glutamine supplements?
The safety of its supplementation during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been well studied. Therefore, it’s best for pregnant or breastfeeding women to avoid supplements unless advised otherwise by their healthcare provider